Targeted nutrition support in COVID-19: In sync with zinc
Dicken Weatherby, N.D. and Beth Ellen DiLuglio, MS, RDN, LDN
Researchers reviewed a number of studies utilizing nutrition or phytochemical prevention or intervention for COVID-19
The ODX COVID-19 Series
- COVID-19: The pandemic that has become endemic
- COVID-19: Overlapping risk factors and chronic disease
- Nutritional status COVID-19: A covert factor in disease susceptibility
- COVID-19: Blood chemistry biomarker patterns - Clues and patterns lurking just under the surface
- COVID-19: Blood chemistry biomarker patterns - Down the research rabbit hole
- COVID-19: Blood Biomarkers - Neutrophils
- COVID-19: Blood Biomarkers - Albumin
- COVID-19: BloodBiomarkers - Cytokines
- COVID-19: Blood Biomarkers - Interleukin-6
- COVID-19: Blood Biomarkers - Interleukin-10
- COVID-19: Blood Biomarkers - Vitamin C
- COVID-19: Blood Biomarkers - Vitamin D
- COVID-19: Blood Biomarkers - Zinc
- Biomarker characteristics and blood type - help sharpen the COVID-19 clinical picture
- COVID-19: Initial indications and conventional interventions
- COVID-19: Long-term risk reduction - Naturopathic, functional medicine, and nutrition-based approaches to prevention
- A healthy diet is primary prevention for COVID-19
- You should have a gut feeling about COVID-19
- Beyond dietary food patterns…plant-based compounds may mitigate COVID-19 risk
- Targeted nutrition support in the battle against COVID-19
- Targeted nutrition support in COVID-19: Armed with vitamin C
- Targeted nutrition support in COVID-19: In sync with zinc
- Targeted nutrition support in COVID-19: Micronutrients and phytonutrients are important players
- Optimal Takeaways for improving immunity and reducing susceptibility to COVID-19
- Optimal - The Podcast: Episode 8 -Blood Biomarkers and Risk Factors for COVID-19 and its Comorbidities
The most promising nutritional and phytochemical compounds being:[i]
- Catechin gallate and gallocatechin gallate
- Elderberry
- Fiber
- Forsythoside
- Melatonin
- Polyphenols
- Probiotics
- Propolis
- Quercetin
- Selenium
- Vitamins A, C, E, D
- Zinc
Effects of several nutrients on aspects of COVID-19 infection. ↑: increase, ↓: decrease
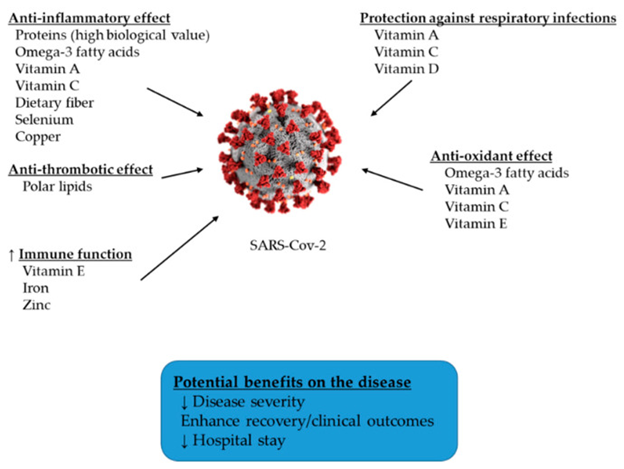
Source: Fernández-Quintela, Alfredo et al. “Key Aspects in Nutritional Management of COVID-19 Patients.” Journal of clinical medicine vol. 9,8 2589. 10 Aug. 2020, doi:10.3390/jcm9082589
Recommended intakes of certain nutrients with key roles in disease susceptibility and the maintenance of an adequate immune function. [ii]
|
Nutrient
|
Immune Function
|
Recommendation
|
|
Healthy Individuals
|
Diseased/Infected Patients
|
|
Vitamin C
|
Maintenance of functional and structural integrity of mucosal cells in innate barriers
Normal functioning of T cells
Antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects
Antibody production
Reduction of respiratory tract and lung infection risk
|
200 mg/day
|
1–2 g/day
|
|
Vitamin D
|
Maintenance of functional and structural integrity of mucosal cells in innate barriers
Normal functioning of T cells
Antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects
Antibody production and antigen responses
Reduction of respiratory tract and lung infection risk
Alleviation of the inflammatory response
|
2000 IU/day (50 µg/day)
|
10,000 IU during few weeks, followed by 5000 IU (until 25–hydroxyvitamin D concentrations rise above 40–60 ng/mL (equivalent to 100–150 nmol/L))
|
|
Vitamin E
|
Maintenance of functional and structural integrity of mucosal cells in innate barriers
Differentiation, and functioning of innate immune cells
Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects
Antibody production and antigen responses
Reduction of respiratory tract and lung infection risk
Support of T cell-mediated immunity
|
15 mg/day (RDA)
|
200 IU/day
|
|
Selenium
|
Differentiation, and functioning, of innate immune cells
Normal functioning of T cells
Antibody production
Antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects
|
50 µg/day
|
Up to 200 µg/day
|
|
Zinc
|
Maintenance of functional and structural integrity of mucosal cells in innate barriers.
Differentiation, and functioning, of innate immune cells.
Antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
Antibody production and antigen response.
Support of lymphocyte and cytokine functions, and innate immunity overall.
Inhibits the activity and replication of coronavirus (SARS-CoV which caused an outbreak in 2002)
|
Men: 8 mg/day
Women: 11 mg/day
(RDA)
|
Zinc lozenges: over 75 mg/day administered within 24 h (divided into 6–8 doses, each separated by 2–3 h when awake)
Zinc gluconate: 13.3 mg/day within 3 days (at least)
|
|
Iron
|
Maintenance of functional and structural integrity of mucosal cells in innate barriers
Differentiation, and functioning, of innate immune cells
Normal functioning of T cells.
Antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects
|
Men: 8 mg/day
Women age 19–50: 18 mg/day
Women age > 51: 8 mg/day
(RDA)
|
Ferrous iron salts (ferrous sulfate and ferrous gluconate): 60 mg Fe/day (taken with food to avoid gastric discomfort)
|
|
Omega-3 fatty acids (EPA + DHA)
|
Conversion to specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) such as, protectins, resolvins and maresins to relieve the inflammation and enhance lung injury
|
250–300 mg/day of EPA + DHA
|
1500–3000 mg/day EPA + DHA
|
|
Multivitamin supplements including vitamins (A, B6, B12, C, D, E and folate) and trace elements (Zn, Fe, Se, Mg and Cu)
|
Support of the cells and tissues of the immune system overall
Maintenance and development of in innate barriers
Growth and differentiation of innate cells
Antibody production and generation of memory cells
Production and activity of antimicrobial proteins
Phagocytic activities of neutrophils and macrophages
|
Supplying nutrient requirements according to the 100% RDA for age and gender
This is in addition to a well-balanced diet
|
Source: Fernández-Quintela, Alfredo et al. “Key Aspects in Nutritional Management of COVID-19 Patients.” Journal of clinical medicine vol. 9,8 2589. 10 Aug. 2020, doi:10.3390/jcm9082589
An entire array of micronutrients factors into the body’s susceptibility to and ability to fight against COVID-19. Each nutrient is a cog in the wheel and should not be overlooked in order to optimize health during this perpetually rampant pandemic.
Next Up - Optimal Takeaways for improving immunity and reducing susceptibility to COVID-19
Research
[i] Ayseli, Yasemin Ipek, et al. "Food policy, nutrition and nutraceuticals in the prevention and management of COVID-19: Advice for healthcare professionals." Trends in Food Science & Technology (2020).
[ii] Fernández-Quintela, Alfredo et al. “Key Aspects in Nutritional Management of COVID-19 Patients.” Journal of clinical medicine vol. 9,8 2589. 10 Aug. 2020, doi:10.3390/jcm9082589
