Welcome to part 4 of the ODX series on "Biological Age: A True Measure of Health." In the fourth post in our series, we will discuss DNA methylation, one of the methods used to measure biological age.
Biological age can be further evaluated using an epigenetic biomarker known as DNA methylation (DNAm). Epigenetics reflects how chemical changes alter how genes are expressed and whether they are turned off or on. DNA methylation refers to adding a methyl group to a specific portion of DNA, which usually turns a gene off or removing a methyl group, which turns a gene on. DNAm also reflects how cells are aging; DNAm patterns can be significantly altered with aging and appear to be associated with cancerous changes (Levine, 2023).
However, potential cofounders associated with DNA methylation evaluation and accuracy include genetic factors, environmental factors, and variations in specific DNAm arrays (Bergsma 2020).
Comparison of chronological vs biological DNAm clocks.
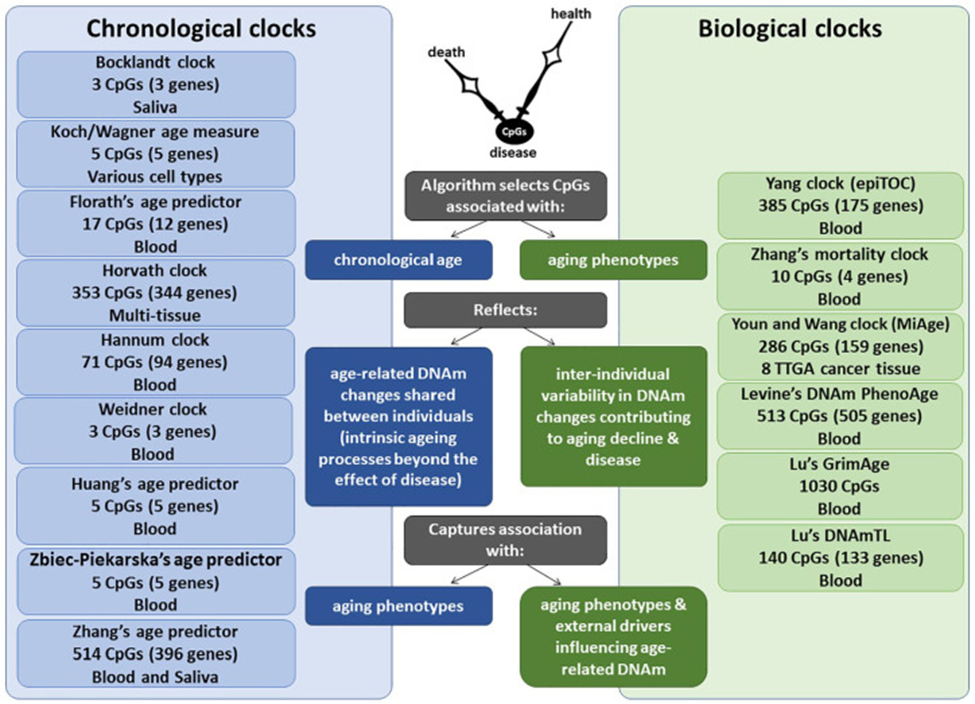
Each DNAm clock is developed using a unique training model, including a variable number of CpGs, tissue source of DNA and corresponding age-related measures. While chronological DNAm clocks reflect age-related DNAm changes that are shared between individuals and are expected to reflect the intrinsic aging process, biological DNAm clocks reflect age-related DNAm changes that vary between individuals and are expected to capture associations with specific age-related phenotypes and external drivers that may influence age-related DNAm.
Source: Bergsma, Tessa, and Ekaterina Rogaeva. “DNA Methylation Clocks and Their Predictive Capacity for Aging Phenotypes and Healthspan.” Neuroscience insights vol. 15 2633105520942221. 21 Jul. 2020, doi:10.1177/2633105520942221 This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 License
DNAm combined with phenotypic (biological) age calculations yield a DNAm PhenoAge. Ultimately, changes in DNAm PhenoAge were highly correlated with changes in biological age, a more straightforward, more attainable equation. Research indicates that DNAm PhenoAge can help predict aging outcomes, including (Levine 2018):
The DNAm PhenoAge was significantly associated with subsequent mortality in 5 large-scale study samples independent of chronological age.
Researchers conclude that increased DNAm PhenoAge, relative to chronological age, is associated with;

Bergsma, Tessa, and Ekaterina Rogaeva. “DNA Methylation Clocks and Their Predictive Capacity for Aging Phenotypes and Healthspan.” Neuroscience insights vol. 15 2633105520942221. 21 Jul. 2020, doi:10.1177/2633105520942221
Levine, Morgan E et al. “An epigenetic biomarker of aging for lifespan and healthspan.” Aging vol. 10,4 (2018): 573-591. doi:10.18632/aging.101414
Levine, Morgan. True Age: Cutting-edge Research to Help Turn Back the Clock. Penguin, 2023.