Essential oils (EOs) have long been used as remedies for various health disorders due to their range of biological activities. They are a subfield of phytotherapy, the use of plant extracts for health benefits, including stress relief, mood enhancement, and promoting a general sense of well-being.
Essential oils possess anti-microbial and anti-inflammatory properties and provide relief from minor discomforts and boost the immune, respiratory, and circulatory systems.
They are classified into several groups according to their scent: citrus, herbaceous, camphorous, floral, woody, earthy, minty, and spicy (Acimovic 2021).
Essential oils demonstrate a wide array of pharmacological effects on the central nervous system (CNS) in particular, including anxiolysis, neuroprotection, antidepressant activity, anticonvulsant effects, and sedation. This makes them potentially viable, safer alternatives or adjuncts to traditional allopathic medications for treating CNS disorders, including insomnia, depression, dementia, and Alzheimer's disease (Soares 2021).
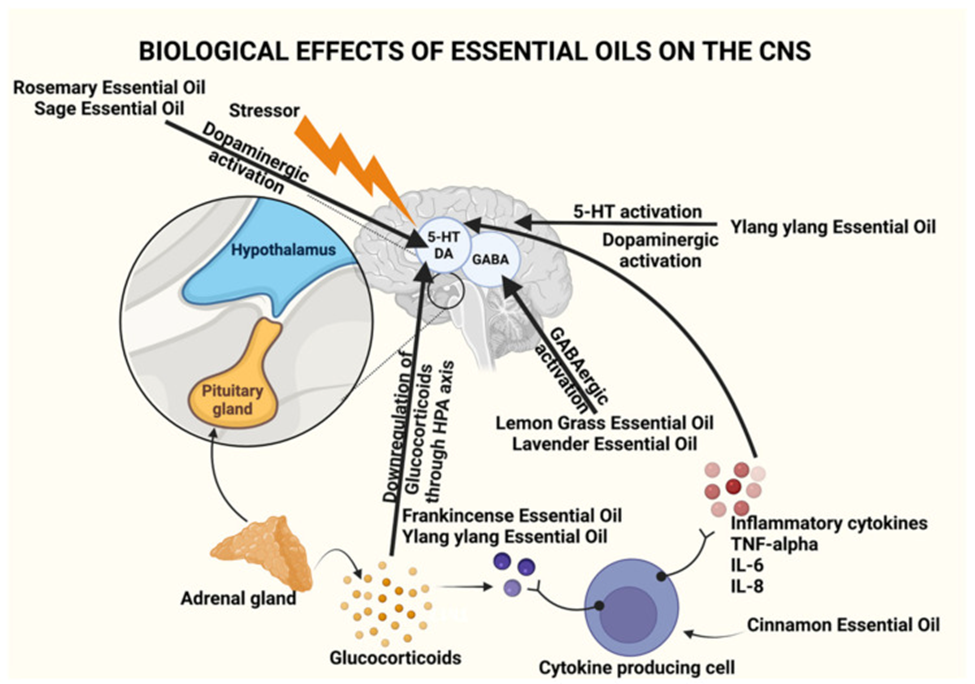
Biological effects of essential oils on the CNS through activation of various components of the brain.
Source: Soares, Giselle A Borges E et al. “Exploring Pharmacological Mechanisms of Essential Oils on the Central Nervous System.” Plants (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 11,1 21. 22 Dec. 2021, doi:10.3390/plants11010021 This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Research indicates EOs' mechanism of action involves direct and indirect interaction with the CNS via various receptor pathways. Notably, EOs containing β-caryophyllene have demonstrated the ability to modulate immune function and inflammatory responses, which is particularly significant in the context of inflammatory conditions such as cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. They also interact favorably with the endocannabinoid system, contributing to improvements in mood and pain relief (Soares 2021).
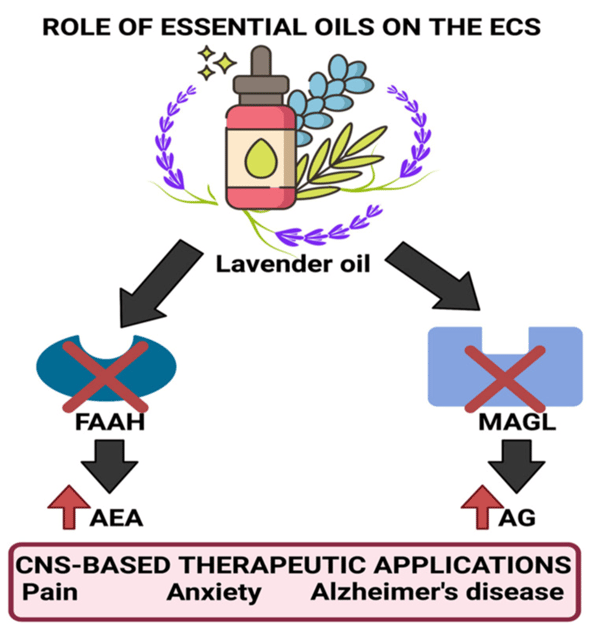
Ability of lavender oil to inhibit the degradation of FAAH and MAGL enzymes, thereby increasing levels of AEA (anandamide) and AG (2-Arachidonoylglycerol), which assist in mood elevation and analgesic effects.
Source: Soares, Giselle A Borges E et al. “Exploring Pharmacological Mechanisms of Essential Oils on the Central Nervous System.” Plants (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 11,1 21. 22 Dec. 2021, doi:10.3390/plants11010021 This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Further, some EOs have shown potential in symptom management associated with neurological diseases and possibly decelerating the disease progression in Alzheimer's patients. Commonly used essential oils that contribute to CNS health and function include frankincense (Boswellia), cinnamon, clove, eucalyptus, lavender, lemongrass, peppermint, rosemary, sage, sandalwood, and Ylang ylang (Soares 2021).
Aćimović, Milica. "Essential oils: Inhalation aromatherapy—a comprehensive review." J. Agron. Technol. Eng. Manag 4 (2021): 547-557.
Soares, Giselle A Borges E et al. “Exploring Pharmacological Mechanisms of Essential Oils on the Central Nervous System.” Plants (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 11,1 21. 22 Dec. 2021, doi:10.3390/plants11010021